A fire on a construction site can result in serious injuries and loss of materials, equipment and even lives. All employees need to be familiar with the jobsite’s fire protection program – who to contact, what to do, the various types of fire extinguishers and their locations throughout the jobsite. Employees should be trained in the use and limitations of fire extinguishers to ensure they are used effectively when needed.
Fire extinguishers are meant to handle only small fires. If a fire becomes too large or the environment becomes too dangerous, employees should evacuate the area.
- The fire is too large.
- The air is unsafe to breathe.
- The environment is too hot or the smoke limits visibility.
- Evacuation paths are impaired.
Keep the fire in front of you. Never place yourself where the fire obstructs your escape.
Classes of Fires and Fire Extinguishers
- A Wood, paper, ordinary trash.
- B Flammable liquids (gasoline, oil, grease, solvents, paints, etc.).
- C Energized electrical equipment.
- D Combustible metals.
- K Kitchen fires.
Use the P.A.S.S. Method for correctly using a fire extinguisher.
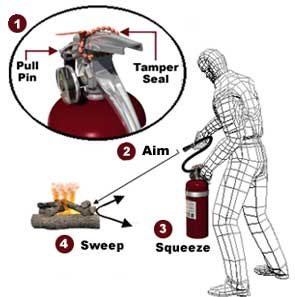
- Pull the Pin – Hold the extinguisher with the nozzle pointing away from you, and release the locking mechanism.
- Aim low – Point the extinguisher at the base of the fire.
- Squeeze the lever slowly and evenly to operate and discharge.
- Sweep the nozzle from side to side.
Fire Extinguisher Inspection
- Visually inspect portable extinguishers or hoses monthly.
- Verify the fire extinguisher is properly charge. Indicator must always be in the green zone.
- Perform an annual maintenance check on portable fire extinguishers and document.
- Fire extinguisher must be easily accessible.
Download the printable PDF and Recording Form here.
Members can download the audio version of this toolbox talk here.
